Home |
Climate Change Project |
Table of Contents |
Courses | Search |
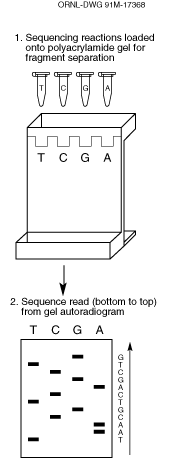
Fig. 12. DNA Sequencing.
Dideoxy sequencing (also called chain- termination or Sanger method) uses an enzymatic procedure to synthesize DNA chains of varying lengths, stopping DNA replication at one of the four bases and then determining the resulting fragment lengths. Each sequencing reaction tube (T, C, G, and A) in the diagram contains
For example, in the A reaction tube the ratio of the dATP to didATP is adjusted so that each tube will have a collection of DNA fragments with a didATP incorporated for each adenine position on the template DNA fragments. The fragments of varying length are then separated by electrophoresis (1) and the positions of the nucleotides analyzed to determine sequence. The fragments are separated on the basis of size, with the shorter fragments moving faster and appearing at the bottom of the gel. Sequence is read from bottom to top (2). (Source: see Fig. 11.)
The Climate Change and Public Health Law Site Provide Website Feedback - https://www.lsu.edu/feedback
The Best on the WWW Since 1995!
Copyright as to non-public domain materials
See DR-KATE.COM for home hurricane and disaster preparation
See WWW.EPR-ART.COM for photography of southern Louisiana and Hurricane Katrina
Professor Edward P. Richards, III, JD, MPH - Webmaster
Privacy Statement - https://www.lsu.edu/privacy
Accessibility Statement - https://www.lsu.edu/accessibility